Secure Gateways: Configuring Mutual TLS using Gateway API on GKE
2025-04-05
Introduction
What Are We Building? 🔐
In this deep dive, we’ll secure traffic to an app on GKE using mutual TLS (mTLS) at the ingress layer with GKE Gateway API. We’ll use self-signed certs to demo client certificate validation—similar to how financial APIs and zero-trust platforms validate service-to-service identity.
Why This Matters
mTLS is core to secure service meshes and external-facing APIs. Validating clients via TLS certs strengthens your perimeter, especially for sensitive workloads.
Scenario Overview
- GKE Autopilot cluster (or standard)
- Gateway API enabled with managed Gateway controller
- One app (
httpbin) behind the Gateway - Server cert (
tls.crt,tls.key) deployed viaSecret - Client cert (
client.crt) validated against a CA bundle (ca.crt) - All certs are self-signed for demo, in real-world you'd use cert-manager or ACM
Architecture
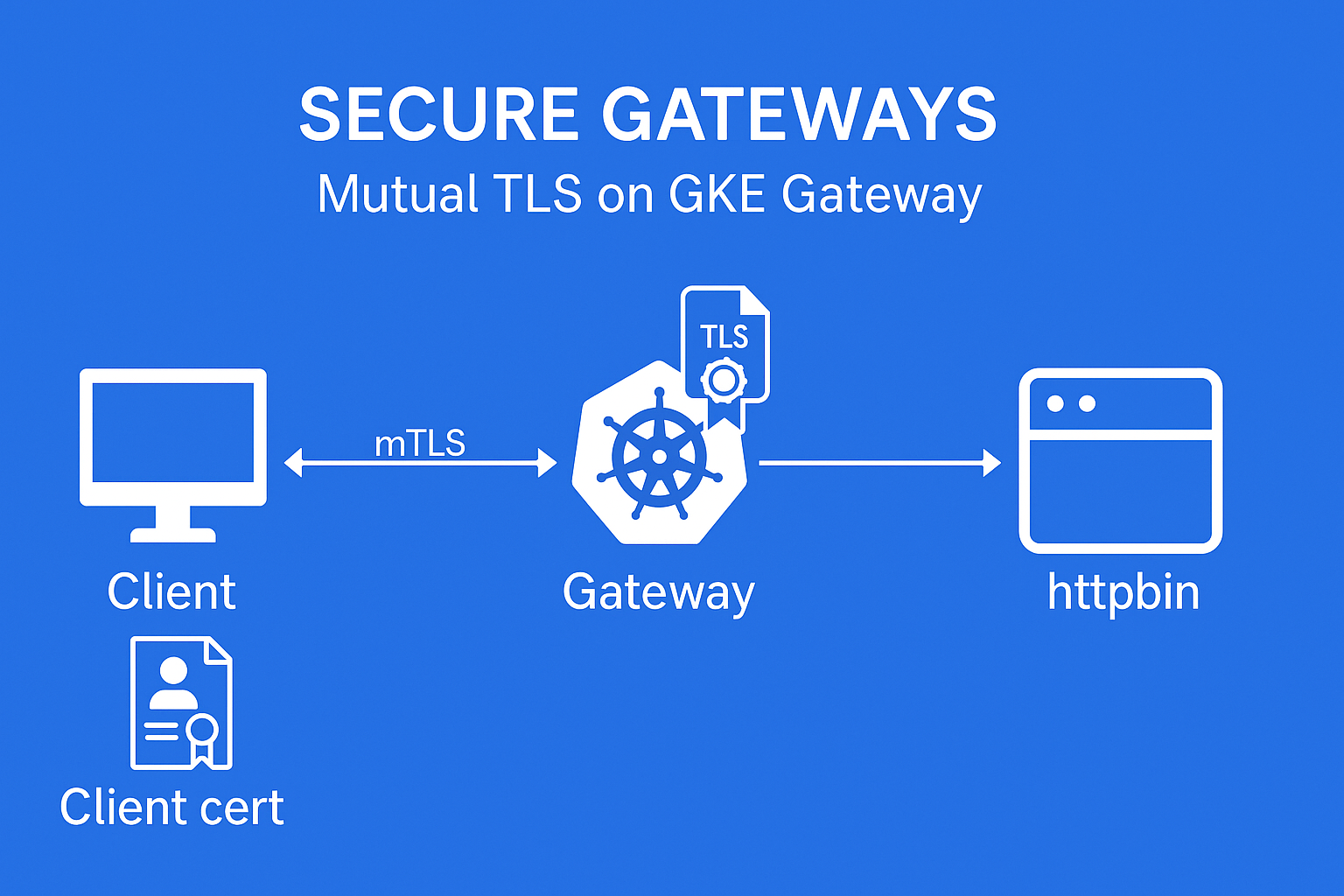
- Gateway only accepts connections where client cert is signed by known CA
- Ingress TLS termination happens at Gateway
- Backend is HTTP (no mTLS between Gateway and app in this example)
Prereqs
- GCP project with billing enabled
gcloud,kubectl,openssl- Gateway API CRDs installed
- GKE cluster with Gateway controller enabled
Step-by-Step Setup
Step 1: Create the Cluster
gcloud container clusters create-auto mtls-demo \ --region us-central1
Enable Gateway API
gcloud container clusters update mtls-demo \ --enable-gateway-api # install CRDs if needed kubectl apply -k "github.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/config/crd/experimental?ref=v1.0.0"
Generate TLS & CA Certs
mkdir certs && cd certs # Create CA openssl req -x509 -nodes -new -sha256 -days 3650 \ -newkey rsa:2048 -subj "/CN=MyCA" \ -keyout ca.key -out ca.crt # Server cert openssl req -new -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -keyout server.key \ -subj "/CN=httpbin.local" -out server.csr openssl x509 -req -in server.csr -CA ca.crt -CAkey ca.key \ -CAcreateserial -out server.crt -days 365 # Client cert openssl req -new -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -keyout client.key \ -subj "/CN=test-client" -out client.csr openssl x509 -req -in client.csr -CA ca.crt -CAkey ca.key \ -CAcreateserial -out client.crt -days 365
Deploy app & secrets
kubectl create ns httpbin kubectl create deployment httpbin --image=kennethreitz/httpbin --port=80 -n httpbin kubectl expose deployment httpbin --port=80 --target-port=80 -n httpbin kubectl create secret tls server-cert \ --cert=certs/server.crt --key=certs/server.key -n httpbin kubectl create configmap ca-cert --from-file=ca.crt=certs/ca.crt -n httpbin
Create Gateway & Routes
Gateway config (gateway.yaml)
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: httpbin-gw
namespace: httpbin
spec:
gatewayClassName: gke-l7-global-external-managed
listeners:
- name: https
port: 443
protocol: HTTPS
tls:
mode: Terminate
certificateRefs:
- kind: Secret
name: server-cert
options:
networking.gke.io/client-verification: "require"
networking.gke.io/trusted-ca: ca-cert
Route config (route.yaml)
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: httpbin-route
namespace: httpbin
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: httpbin-gw
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /
backendRefs:
- name: httpbin
port: 80
Apply the configs:
kubectl apply -f gateway.yaml kubectl apply -f route.yaml
Test the setup
Get IP address of the Gateway:
kubectl get gateway -n httpbin
Let’s test with and without the client cert.
✅ Valid client
curl --cert certs/client.crt --key certs/client.key --cacert certs/ca.crt \ https://<GATEWAY_IP>/get
❌ No client cert
curl --cacert certs/ca.crt https://<GATEWAY_IP>/get
Expected: 400 or 403 depending on GKE's enforcement.
Automated Testing (Optional)
Create a script to automate the testing.
#!/bin/bash URL=https://<GATEWAY_IP>/get curl --silent --cert certs/client.crt --key certs/client.key --cacert certs/ca.crt $URL | grep "headers" if [ $? -ne 0 ]; then echo "mTLS test failed"; exit 1; fi echo "mTLS test passed"
Key Takeaways
- GKE Gateway API supports native mTLS client validation via annotations
- Certs must be manually injected via Secret and ConfigMap
- Only valid clients (with signed certs) can connect
This pattern is extendable to service meshes, APIs, and zero-trust networking
Code
Conclusion
You now have a secure GKE Gateway that validates clients using mutual TLS. In the next part, we'll explore using cert-manager for automated cert issuance and chaining this setup with an internal-only backend.
